
- Computer Fundamentals
- Computer - Home
- Computer - Overview
- Computer - Advantages & Disadvantages
- Computer - Classification
- Computer - Applications
- Computer - History and Evolution of Computers
- Computer - System Characteristics
- Computer - Origins
- Computer - Generations
- Computer - Types
- Computer - Components
- Computer - CPU
- Computer - Input Devices
- Computer - Output Devices
- Computer - Memory Units
- Computer - Hardware
- Computer - Motherboard
- Computer - RAM
- Computer - Read Only Memory
- Computer - Software
- Computer - Software Types
- Computer - Data Storage and Memory
- Computer - Memory
- Computer - Internet and Intranet
- Computer - Internet
- Computer - Extranet
- Computer - Websites
- Computer - Word Processors
- Computer - Spread Sheet
- Computer - Power Presentations
- Computer - E-mail Tools
- Computer - Ports
- Computer - Number System
- Computer - Number Conversion
- Computer - Data and Information
- Computer - Networking
- Computer - Operating System
- Computer - Keyboard Shortcut Keys
- Computer - Antivirus
- Computer - Virus
- Computer - How to Buy?
- Computer - Available Courses
- Computer Useful Resources
- Computer - Quick Guide
- Computer - Useful Resources
- Computer - Discussion
Computer Fundamentals - Computer Ports
What are Computer Ports?
The computer ports are physical docking points of a computer that facilitate users to connect required external devices to the computer or computer network. A connection point that acts as an interface between the computer and external devices like a mouse, printer, modem, etc. is called a port. Ports are of two types −
- Internal port − It connects the motherboard to internal devices like hard disk drives, CD drives, internal modems, etc.
- External port − It connects the motherboard to external devices like modem, mouse, printer, flash drives, etc.
Expansion of a computer network or interconnection between multiple peripheral devices was possible through computer ports where network connections start and end. Generally, Ports are computer hardware which are software-based means they are operated by a software program like an operating system.
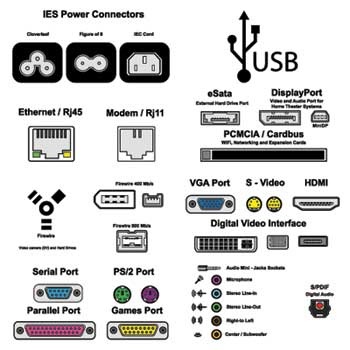
The below image gives an idea about what ports are look like −
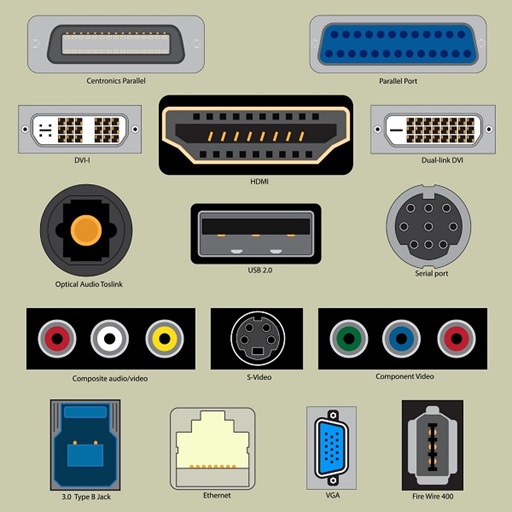

Fig: Some most commonly used computer/ networking ports
Generally, ports are docking points through which information flows from a program to the computer or over the Internet.
Working Principles of Computer Ports
Computer ports are tangible or virtual connectors on a computer or device that provide connectivity to external devices, peripherals, or networks. They enable the exchange of information between the computer and external devices.
The functions or working principles of some common computer ports are as follows −
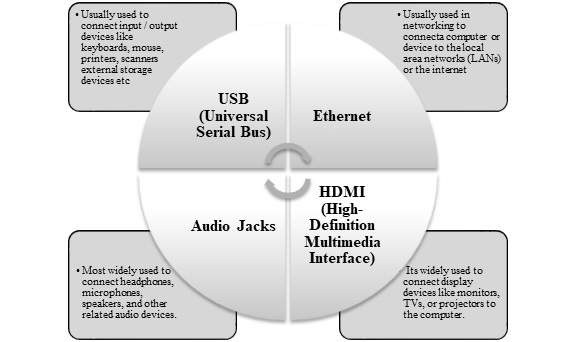
Fig: Functions of computer ports
Thunderbolt − These allow peripherals such as external storage, monitors and docking stations to be connected at high speed. Thunderbolt ports, which were created by Intel and Apple, allow for fast data transfer as well as the carrying of power and video. USB-C connectors are frequently used with Thunderbolt 3 ports.
| Thunderbolt | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Physical Connection i. Ports are physical sockets ii. Fixes on computer or devices to plug cables or connectors from external devices iii. Cables have connectors at both ends, one to fit into the port on the computer and the other to fit into the external device. |
Data Transfer i. Once the device connected to a port, data can be transferred between the computer and the device. ii. Allows transferring files to and from external storage devices iii. Sending and receiving data over a network connection iv. Streaming audio and video to external devices. |
Communication Protocols i. Port uses specific communication protocols to transfer data ii. For example, USB, which offers different data transfer speeds and capabilities, uses protocols such as USB 3.0, USB 3.0C, and USB 2.0C, each of which offers different data transfer speeds and capabilities. |
Device Recognition i. The device is recognised by the computer and drivers and automatically install drivers or configure settings to support it For example, when we connect a USB mouse, the system detects it automaticall and enables pointer control. |
Power Supply i. Ports provide power to connected devices. For example Smartphones, tablets, and USB accessories can be powered using USB ports without an adapter. |
Overall, Computer ports allow the computer to communicate and transfer data with external devices and peripherals.
Characteristics of Ports
A port has the following characteristics −
- External devices are connected to a computer using cables and ports.
- Ports are slots on the motherboard into which a cable of the external device is plugged in.
- Examples of external devices attached via ports are the mouse, keyboard, monitor, microphone, speakers, etc.
Let us now discuss a few important types of ports −
Serial Port
In the past, it was used to connect different devices which includes modems, mice, and printers; however, due to the prominence of USB, it has become completely obsolete in modern computers. Serial ports transmit data sequentially means one bit at a time. To do the same, these ports require one cable to transmit 8 bits. However, this makes slower communication. Serial ports are usually having 9-pin or 25-pin male connectors. They are also known as COM (communication) ports or RS323C ports.

Overall, serial ports act as a port which is −
- Used for external modems and older computer mice
- Two versions: 9-pin, 25 pin model
- Data travels at 115 kilobits per second
Parallel Ports
Another older port that is primarily used for connecting printers and other devices that are used for external storage; like serial ports, parallel ports are rarely found on modern computers. Parallel ports can send or receive 8 bits or 1 byte at a time. Parallel ports come in the form of 25-pin female pins and are used to connect printers, scanners, external hard disk drives, etc.

- Used for scanners and printers
- Also called a printer port
- 25 pin model
- IEEE 1284-compliant Centronics port
PS/2 Port
PS/2 stands for Personal System/2. It is a female 6-pin port standard that connects to the male mini-DIN cable. PS/2 was introduced by IBM to connect Input/output peripherals to personal computers. Used to create a connection between keyboards and mice on computers that is of an earlier generation. PS/2 ports have a circular shape, and they are coloured purple for keyboards and green for mice.
This port is now mostly obsolete, though some systems compatible with IBM may have this port.

- Used for old computer keyboard and mouse
- Also called the mouse port
- Most of the old computers provide two PS/2 ports, each for the mouse and keyboard
- IEEE 1284-compliant Centronics port
Universal Serial Bus (or USB) Port
USB stands for Universal Serial Bus. It is the industry standard for short-distance digital data connection. It is one of the most popular ports for connecting accessories, including external hard drives, printers, mice, keyboards, and more. There are different types and sizes of USB ports, such as micro-USB, USB-A, USB-B, and USB-C.USB port is a standardized port to connect a variety of devices like printers, cameras, keyboards, speakers, etc.

Overall, a USB port acts as a port which is −
- It can connect all kinds of external USB devices such as external hard disks, printers, scanners, mice, keyboards, etc.
- It was introduced in 1997.
- Most of the computers provide two USB ports as a minimum.
- Data travels at 12 megabits per second.
- USB-compliant devices can get power from a USB port.
VGA (Video Graphics Array) Port
Before the development of DVI, HDMI and DisplayPort, VGA was in use; it's an analogue interface between a computer and the monitor. It's a display standard developed by IBM in 1987; VGA replaced the existing digital CGA and EGA interfaces with a smaller resolution and fewer colours. A standard VGA works on 16-color displays with a refresh rate of 60 Hz and a resolution of 640 × 480. There are 256 colours shown if the resolution is lowered to 320 x 200. Nowadays, it's not in use, older PCs and displays have this video port. Digital connections like HDMI and DisplayPort are replacing it.

Overall, a VGA port acts as a port that −
- Connects monitor to a computer's video card.
- It has 15 holes.
- Similar to the serial port connector. However, the serial port connector has pins, VGA port has holes.
Power Connector
For the sole purpose of supplying power to a device, power connectors are devices that allow an electrical current to pass through them.

It is possible for a computer or other electronic device to charge its battery and get power from a wall outlet through its power port. Since desktop computers don't have batteries, they can't be turned on without a power cord plugged into the power port. The battery in a device like a laptop can work even if nothing is plugged into the power port as long as the battery is charged.
Overall, a power connectors port acts as a port which is a
- Three-pronged plug.
- Connects to the computer's power cable that plugs into a power bar or wall socket.
Firewire Port
An interface with a high data transfer rate is generally utilized for connecting digital camcorders, external hard drives, and other multimedia equipment. USB and Thunderbolt have mostly superseded it. Hence, a FireWire is a high-speed computer data transfer interface that is used to connect personal computers, audio and video devices, as well as other professional and consumer electronic products.

Overall, a FireWire port acts as a port which is a
- Transfers large amounts of data at a very fast speed.
- Connects camcorders and video equipment to the computer.
- Data travels at 400 to 800 megabits per second.
- Invented by Apple.
- It has three variants: 4-Pin FireWire 400 connector, 6-Pin FireWire 400 connector, and 9-Pin FireWire 800 connector.
Ethernet Port
An Ethernet port also known as a jack or socket is a port used to access the internet on commuter. Enables wired network connections, which are normally used for connecting computers to routers, switches and modems that allow Internet access. It's like computer network equipment that Ethernet cables plug into. The main goal of this port is to connect wired network hardware in an Ethernet LAN, MAN, or wide WAN.

- Connects to a network and high-speed Internet.
- Connects the network cable to a computer.
- This port resides on an Ethernet Card.
- Data travels at 10 megabits to 1000 megabits per second depending upon the network bandwidth.
SD Card Slot
SD card slots are frequent functionality ports generally seen on desktop computers and laptops.

These slots enable users to insert SD memory cards, which are typically utilized in digital cameras and other portable devices.
To Continue Learning Please Login